计算机网络自顶向下方法Character1
本文概述:
本文主要记录计算机网络自顶向下方法第一章节的知识点。
学习书籍为:计算机网络自顶向下方法
学习视频为:国立清华大学黄能富教授讲解的计算机网络自顶向下方法,需要的可以点击 这里
What’s the Internet: nuts and blots view
终端(host) = end-systems: running network apps
通信线路(communication links): transmission rate = bandwidth 带宽
路由器(routers): forward packets
Protocols(协议): control sending, receiving of messages: TCP/IP, HTTP, Skype, 802.11
Internet: network of networks: Interconnected ISPs
Internet standards: RFC: Request for comments/ IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force.
What’s the Internet: a service view
communication infrastructure that provides services to application: Web, VoIP, email, games, e-commerce, social nets… 通信基础建设,分散式应用(enbales distributed)
provides programming interface to apps:
allow sending and receiving app programs to connect to Internet.
provides service to options, analogous to postal service.(提供选项服务,类似于邮政服务。)
communication services provided to application:
connectionless / connection-oriented
What’s a protocol:
- Define: format, order of messages sent and received among network entities
- actions taken on message transmission, receipt of a message.
- machines rather than humans;
- all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols
A closer look at network structure:
network edge: applications and hosts e.g. phone
networl core: routers/ network of networks
access networks, physical media: communication links
The network edge:
- end systems(hosts)
- run application programs: Web/ email
- client/server model 主从结构
- client host requests, receives. service from always-on server like web browser/server or email client/server
- peer-peer(P2P) model(UDP): minimal(or no) use of dedicated servers eg: KaZaA 不使用server
connection-oriented service:
- Goal: data transfer between end systrems
- handshaking(握手): set up(prepare for) data transfer ahead of time; set up “state” in two communicating hosts.
- TCP- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP service): Internet’s connection-oriented service
- reliable(内容正确,数量正确,顺序正确);
- in-order byte-stream data transfer: problem: loss: acknowledgements(一定要回答收到) and retransmissions(如果没有回答,重新发送).
- flow control(流量控制) : sender won’t overwhelm receiver. 发送者不知道接收者的承载能力,一直发送,导致接收者崩溃,因此需要流量控制。receiver控制(告诉)sender能发多少。
- congestion control(拥塞控制): sender “slow down sending rate” when network congested. 发生拥挤,就放慢传送速度
conectionless service
- Goal: data transfer between end systems
- UDP: User Datagram Protocol. Internet’s connctionless service: unreliable data transfer; no flow control; no congestion control
TCP/UDP
App‘s using TCP: HTTP(web), FTP(file transfer), Telnet(remote login), SMTP(email)
App’s using UDP: streaming media, teleconferencing, DNS (域名系统), Internet telephony.
The Network Core:
mesh of inetrconnected routers (网状路由器)
Q: The fundamental question: how is data transfered throught net?
A: circuit switching: dedicated circuit per call: telephone net
packet-switching: data sent thru (直通) net in discrete “chunks”(大块)Circuit switching
End-end resources reserved for “call”:
link bandwidth, switch capacity
dedicated resources: no sharing 每一个call都是专属的,专用的
circuit-like (guaranteed) performance
call setup required.
network resourcs divided into “pieces” (pieces allocated to calls; resource piece idle if not used by owning call (no sharing) 资源块空闲如果不被使用的话)
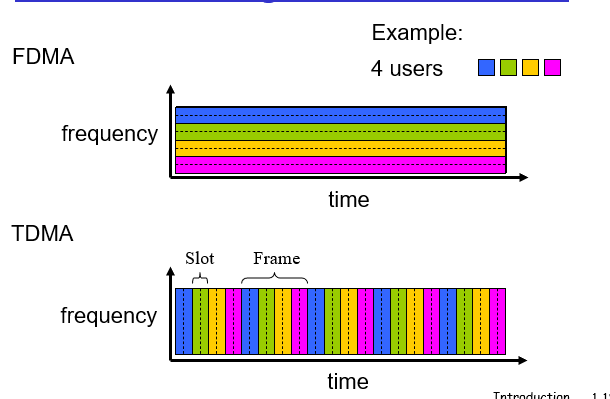
dividing link bandwidth into “pieces”. (frequency division/ time division) 时间和频率两种分割方式
Packet switching (不要固定的线路不要固定的时间)
each end-end data stream divided into packets
user A, B packets share network resources
each packet used full link bandwidth
resources used as needed
resource contention: aggregate resource demand can exceed amount available; congestion: packets queue, wait for link use; store and forward: packets move one hop at a time (transmit over link; wait turn at next link)
Sequence of A & B packets does not have fixed pattern —> Statistical multiplexing
In TDM each host gets some slot in revolving TDM frame.
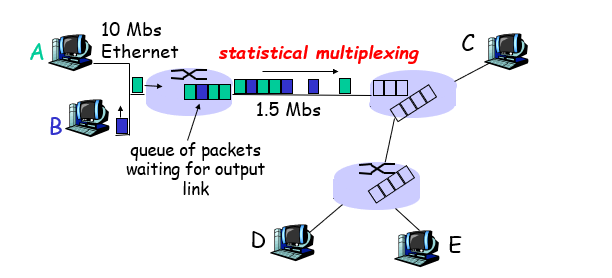
Packet switching VS Circuit switching
Packet switching allows more userd to use network!
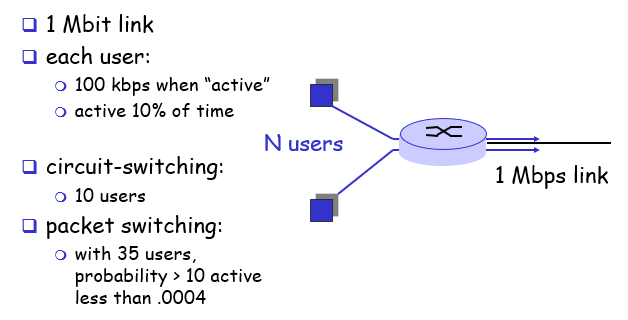
Is packet switching a “slam dunk winner?” 不管什么时候,packet switching都是最好的吗?
- Great for bursty data (爆发性短暂的data): resource shraing; simpler, no call setup
- Excessive congestion: packet delay and loss: protocols needed for reliable data transfer, congestion control
How to provide circuit-like behavior?
- bandwidth guarantees needed for audio/video apps
- still an unsolved problem.
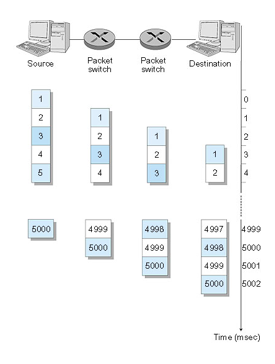
store-and-forward 存储转发
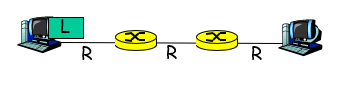
Takes L/R seconds to transmit (push out) packet of L bits onto a link of R bps.
Entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link: store and forward
Message Segmenting
pipelining: each link works in parallel
- Forwarding
- Goal: moveing packets through routerd from source to destination
- datagram network:
- destination address(IP) in packet determines next hop
- routes may change during session
- analogy: driving, asking directions
- virtual circuit network: 不是专用的线路,是固定的
- Each packet carries tag (virtual circuit ID), tag determines next hop
- Fixed path determined at call setup time (一定有建立联系的时间), remains fixed thru call(通过通话保持固定)
- routers maintain per-call state
Network Taxonomy
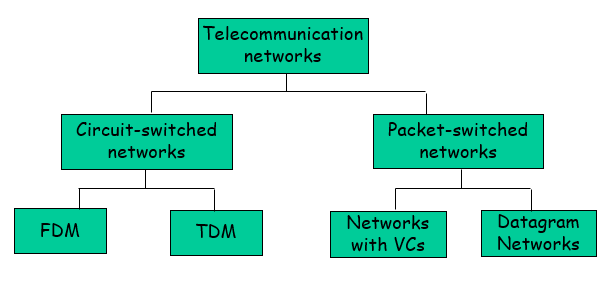
固定路线:
FDM: 按频率分,不分享,专属resource
TDM: 按时间分,不分享,专属resource
不固定路线:
Networks with VCs: 不固定的情况下走固定的路线使用Virtual Circuits. 人工的方式走固定路线,tag
Datagram network: 每一个都带着destination address, 具体路线看router. router有一个很大的动态表。
Datagram network is not either connection-oriented or connectionless.
Internet provides both connection-oriented (TCP) and connectionless services (UDP) to apps.
Access networks and physical media:
- Q: How to connect end systems to edge router? 如何将终端系统连接到边缘路由器?
- residential access nets
- insititutional access networks
- mobile access networks
Residential access: point to point access
- Dialup via modern: 56kbps; Can’t surf and phone at the same time: can’t be always on
- ADSL: asymmetric digital subscriber line非对称数字用户线: up to 1 Mbps upstream (today typically < 256 bps); up to 8 Mbps downstream(today typically < 1 Mps); FDM: 50 kHz ~ 1 Mhz for downstream/ 4 kHz ~ 50 kHz for upstream/ 0 kHz ~ 4 kHz for ordinary telephone 非对称性,上传下载。 线路上可以有很多的频道。
Residential access: cable modems同轴电缆
- HFC: hybrid fiber coaxial cable 光纤和同轴电缆混合在一起的结构
- asymmetric: up to 30Mbps downstream, 2 Mbps upstream
- network of cable and fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- shared access to router among home
- issues: congestion, dimensioning 规模大
- deployment部署: available via cable companies, e.g., MediaOne
Institutional access networks(School, company):
- company/university local area network (LAN) connects end system to edge router.
Wireless access networks: shared wireless access network connects end system to router
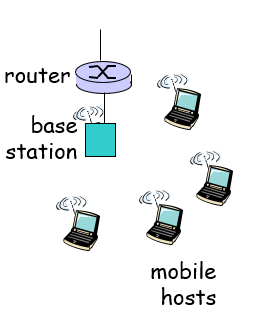
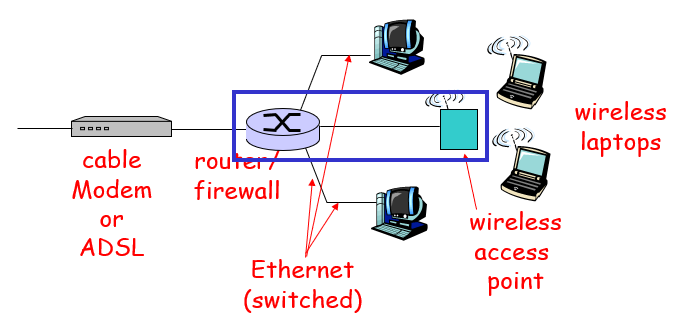
Home networks
Typical home network components:
ADSL or cable modem
router/ firewall/ NAT
Ethernet
wireless access point
Physical Media
Bit: propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs 在发射器/接收器对之间传播
physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver
guided media: signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
unguided media: signals propagate freely, e.g., radio
Twisted Pair (TP) 双绞线
two insulated copper wires
Category 3: traditional phone wires, 10 Mbps Ethernet
Category 5 TP: 100Mbps Ethernet
Coaxial cable:双向传输
- two concentric copper conductors
- bidirectional
- baseband: single channel on cable; legacy Ethernet
- broadband: multiple channels on cable; HFC
Fiber optic cable:
- glass fiber carrying light pulses(光的脉冲), each pulse a bit
- high-speed operation: high-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 5 Gps)
- low error rate: repeaters spaced far apart ; immune to electromagnetic noise
Radio:
- signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum
- no physical “wire”
- bidirectional
- propagation environment effects: reflection; obstruction by objects; interference
- Link Types:
- terrestrial microwave
- LAN(e.g. WIFI)
- wide-area(e.g. cellular)
- satellite
Internet structure: network of networks
ISP: Internet Service Provider
At center “Tier 1 ISPs”(e.g. UUNet,BBN/Genuity, Sprint, AT&t), national/international coverage
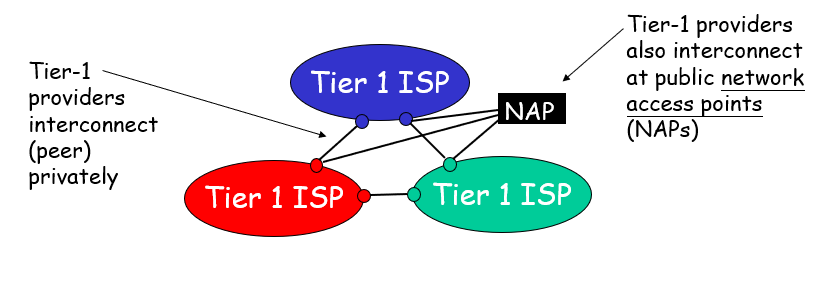
“Tier-2 ISPS”: smaller (oftrn regional) ISPs(Connect to one or more tier-1 ISPs, possibly other tier-2 ISPs
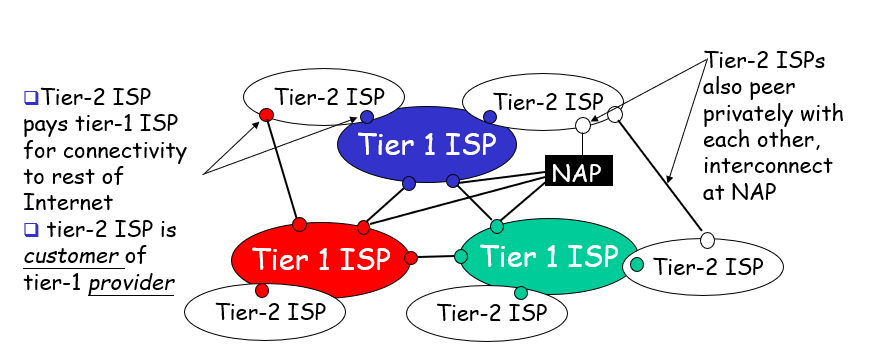
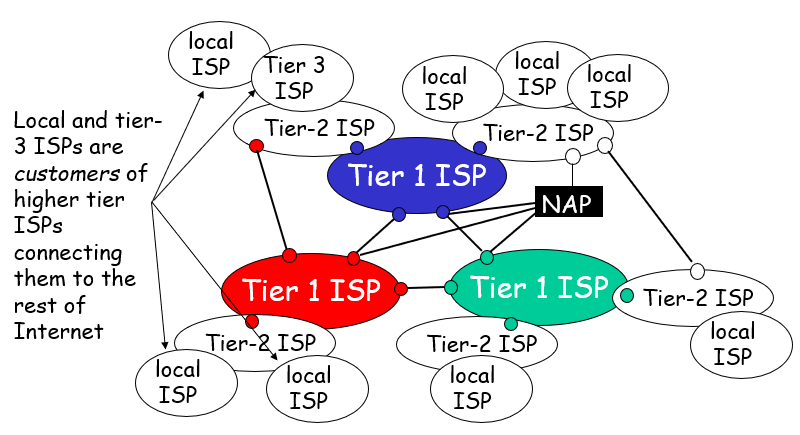
“Tier-3” ISPs and local ISPs (last hop(access) network (closest to end systems))
Delay & Loss
How do loss and delay occur?
packets queue in router buffera
Packet arrival rate to link exceeds output link capacity
Packets queue, wait for turn
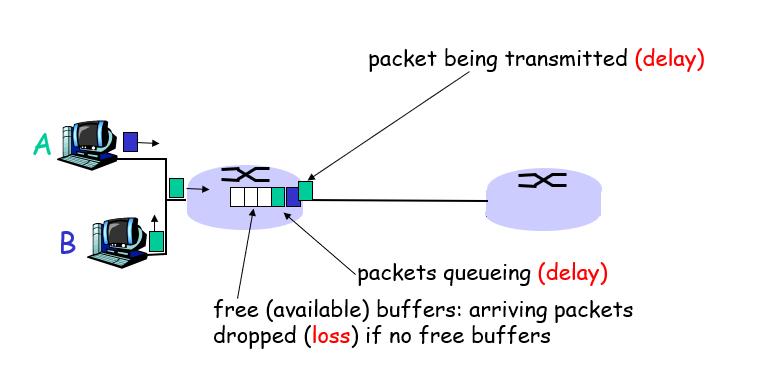
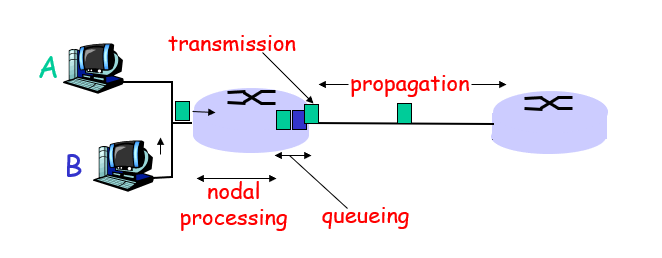
Four source of packet delay
nodal processing:
- check bit errors
- determine output link (查表检查)
queueing
time waiting at output link for transmission
depends on congestion level of router
Transmission delay:
- R = link bandwidth(bps)
- L = packet length(bits)
- time to send bits into link = L/R
Propagation delay(传播延时)
d = length of physical link
s = propagation speed in medium
propagation delay = d/s
*Note: *s and R are very different quantities
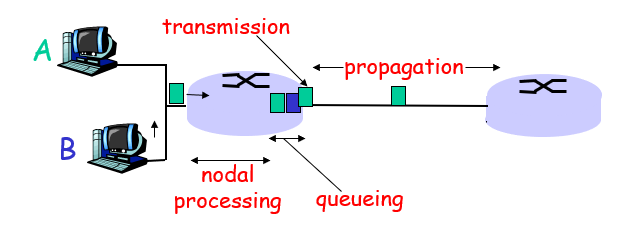
Nodal Delay:
dproc = processing delay: typically a few microsecs or less
dqueue = queuing delay: depends on congestion
dtrans = transmission delay: m= L/R, significant for low-speed links
dprop = propagation delay: a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs
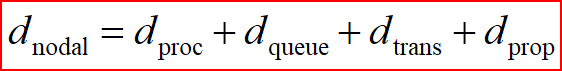
Queueing Delay:
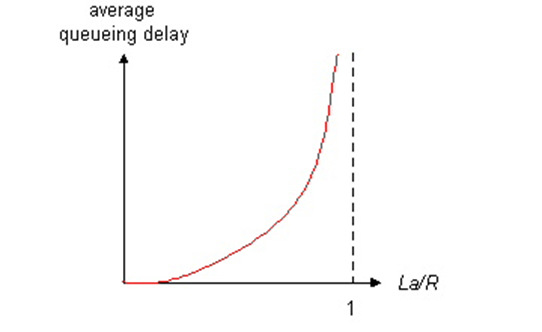
R = link bandwidth (bps)
L = packet length (bits)
a = average packet arrival rate
L * a = average bit arrival rate
traffic intensity = (L * a)/R
- traffic intensity ~ 0: average queueing delay small (包来的数量很少)
- traffic intensity -> 1: delays become large (queue已经快满了)
- traffic intensity > 1 : more “work” arriving than can be serviced, average delay infinite! (infinite queue length) – or packet loss! (finite queue length) (这意味着queue已经满了,出的比入的要少)
“Real” Internet delays and routes:
- Traceroute program (路径追踪):provides delay measurement from source to router along end-end Internet path towards destination.
Protocol layers, servie models
Why layering?
Dealing with complex systems:
- explicit structure allows identification, relationship of complex system’s pieces; layered reference model for discussion
- modularization eases maintenance, updating of system
- change of implementation of layer’s service transparent to rest of system
Internet protocol stack
application: supporting network applications (FTP, SMYP, HTTP)
transport: host-host data transfer (application to application)
- TCP(用不可靠的环境提供可靠的传输),UDP
network: routing of datagrams from source to destination 一个source送到一个目的地,可能会经过几十个router,路径选择,好坏,随时变换
- IP, routing protocols
link: data transfer between neighboring network elements 两点之间的传送
- PPP, Ethernet
physical: bit “on the wire”
Layering: logical communication (e.g. transport)
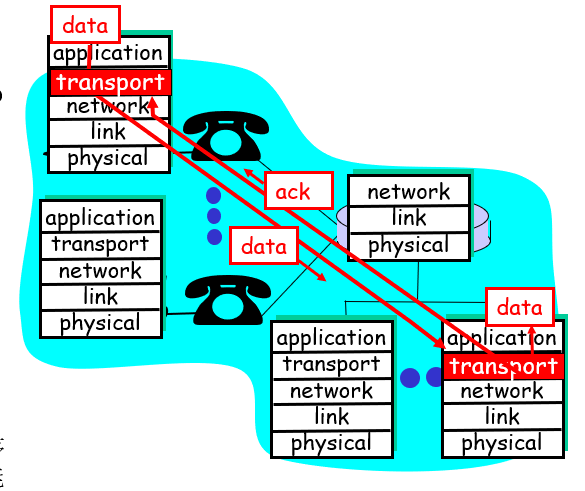
- take data from app
- add addressing, reliability check info to form “datagram”
- send datagram to peer
- wait for peer to ack receipt
- e.g. post office
- 资料要对,先后顺序要对,不能多也不能少,量也要对。
Layering: physical communication
这里就直接摆过程了
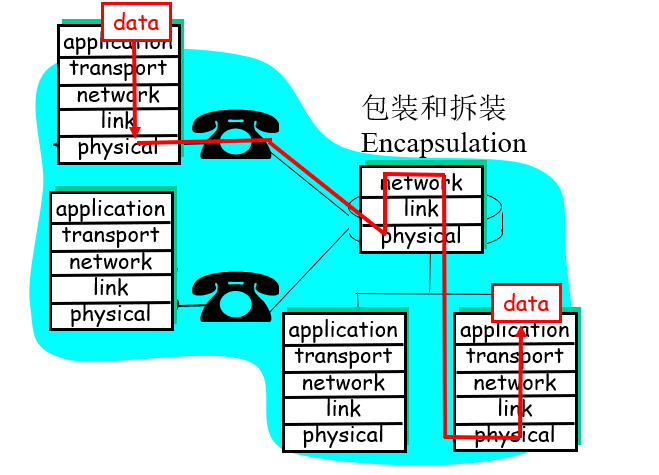
此过程中,较为重要的是当data到达路由器时进行的包装和拆装过程,即Encapsulation
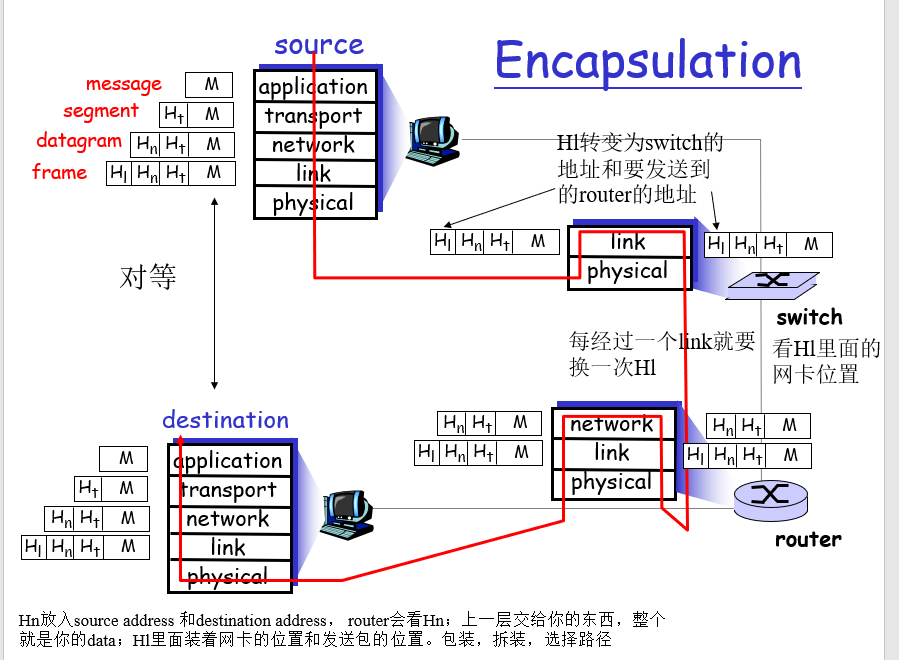
如上图所示,当Hn放入source address 和 destination address, router会解析Hn;上一层交付的东西,整体为传输的data;HI中存储着网卡的位置和发送包的位置。